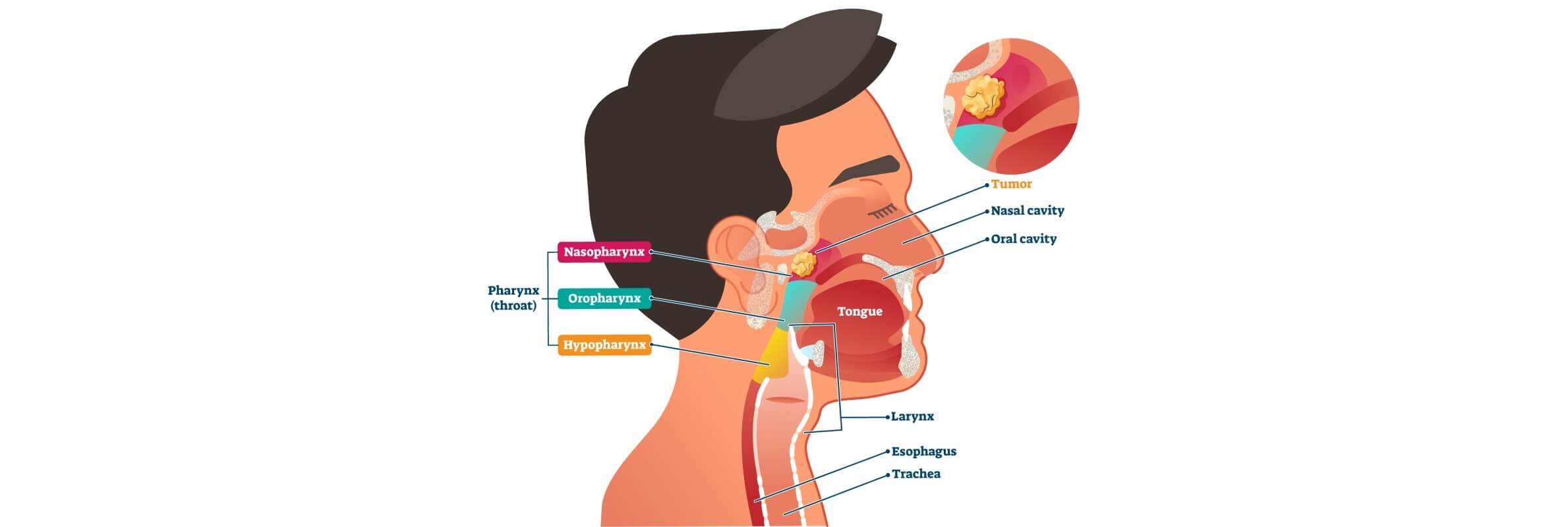
Nasopharyngeal cancer – is a malignant neoplasm of the head and neck that develops in the anatomical area of the nasopharynx and has clear etiological, histological and clinical features. Unlike other tumors of this localization, the nasopharynx tumor is often associated with Epstein-Barr virus and has characteristic pathways [1].
From an anatomical point of view, the tumor process most often occurs in the Rosenmuller's fossa, which explains the late detection of the disease and the high risk of regional metastasis of nasopharynx carcinoma. At the cellular level, nasopharynx carcinoma cells show varying degrees of differentiation depending on the histological subtype.
Types of nasopharyngeal cancer
Nasopharynx tumor has characteristic histopathological features that distinguish nasopharynx carcinoma from other head and neck tumors. According to the WHO classification, nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging at the morphological level is based on the division of the tumor into three main histological subtypes.
Type 1. Keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
The keratinizing variant of nasopharyngeal tumor is histologically indistinguishable from squamous cell nasopharyngeal carcinoma of other anatomical localizations. The tumor exhibits distinct squamous cell differentiation with pronounced cell-to-cell bridges and variable keratinization, including the formation of keratin pearls. Depending on the degree of keratinization, nasopharyngeal tumor cells can be well, moderately or poorly differentiated, which is important when assessing the course of the disease [2].
Type 2. Nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
The nonkeratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma is characterized by cords or trabeculae of interconnected cells with distinct boundaries and minimal or no keratinization. A desmoplastic reaction is usually absent, but a lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate is often identified in the stroma, which is characteristic of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Type 3. Undifferentiated or poorly differentiated carcinoma
Undifferentiated nasopharynx carcinoma when stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) shows one of two morphological patterns that do not affect the prognosis of nasopharynx carcinoma:
Regaud pattern – cohesive cells with indistinct boundaries forming syncytial structures. Schmincke pattern – non-cohesive cells with diffuse infiltrative growth that can mimic the lymphoproliferative process. Cells of this subtype of nasopharynx tumor cells usually have rounded nuclei with pronounced nucleoli. Lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate is often found in the surrounding tissues, which is typical for virus-associated forms of nasopharyngeal carcinoma [3].
Nasopharyngeal cancer stage
Staging of nasopharynx carcinoma is based on the TNM system and allows accurate assessment of the anatomical distribution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, the degree of regional damage and the presence of distant metastases. The results of nasopharyngeal tumor staging are crucial for selecting nasopharyngeal cancer treatment methods and predicting the course of the disease.
Staging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma is based on the TNM system and allows for a comprehensive assessment of the prevalence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which is critical for the selection of nasopharyngeal cancer treatment. In the early stages, developing nasopharynx carcinoma can be asymptomatic, and early stage nasopharyngeal cancer is usually limited to the nasopharynx or adjacent parts without damage to the parapharyngeal space. As nasopharyngeal carcinoma spreads progress to the parapharyngeal space, adjacent muscles, and bone structures of the skull base, reflecting a shift to locally common forms of the disease. Cancer cells are able to spread early through the lymphatic system, which explains the frequent involvement of the cervical lymph nodes in the early stages of the disease.
One characteristic of nasopharynx tumors is its early lymphogenic distribution, as nasopharyngeal tumor cells have high metastatic activity. Damage to cervical and retropharyngeal lymph nodes without distant metastases often corresponds to nasopharyngeal carcinoma stage 3, while massive local spread or invasion into critical anatomical structures is usually classified as stage 4 nasopharynx carcinoma. The appearance of distant metastases means the systemic process and formation of the metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer.
The results of nasopharynx carcinoma staging directly determine the strategy of nasopharyngeal cancer treatment. Localized forms allow effective treat of nasopharyngeal cancer through radiotherapy, while common stages, recurrent nasopharynx carcinoma or cases requiring treatment for stage 4 nasopharyngeal cancer require combined approaches. In such situations, modern nasopharyngeal cancer treatment options, including proton beam therapy nasopharynx carcinoma, play a key role in achieving local control and reducing treatment toxicity.
Diagnosis and tests for nasopharyngeal cancer
Careful collection of anamnesis and physical examination of the head and neck are fundamentally important and determine the further scope of diagnostic measures. If a suspicious mass is found in the mouth, oropharynx, thyroid gland, or hypopharynx, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the neck with intravenous contrast should be performed. CT well identifies bone invasion and allows assessment of appropriate regional lymphatic basins, and is often necessary for radiotherapy planning [4]. At the same time, CT is less accurate in assessing the prevalence of soft tissue injury and its resolution may not be sufficient to detect extremely small tumors, whereby magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography combined with CT (PET-CT) may be more informative [5].
MRI of the face and neck is the best method to estimate primary tumor prevalence (T-stage) as accurately as possible. Histological verification is mandatory for accurate staging and treatment planning. It is usually performed by endoscopic biopsy of nasopharynx formation under local or general anesthesia.
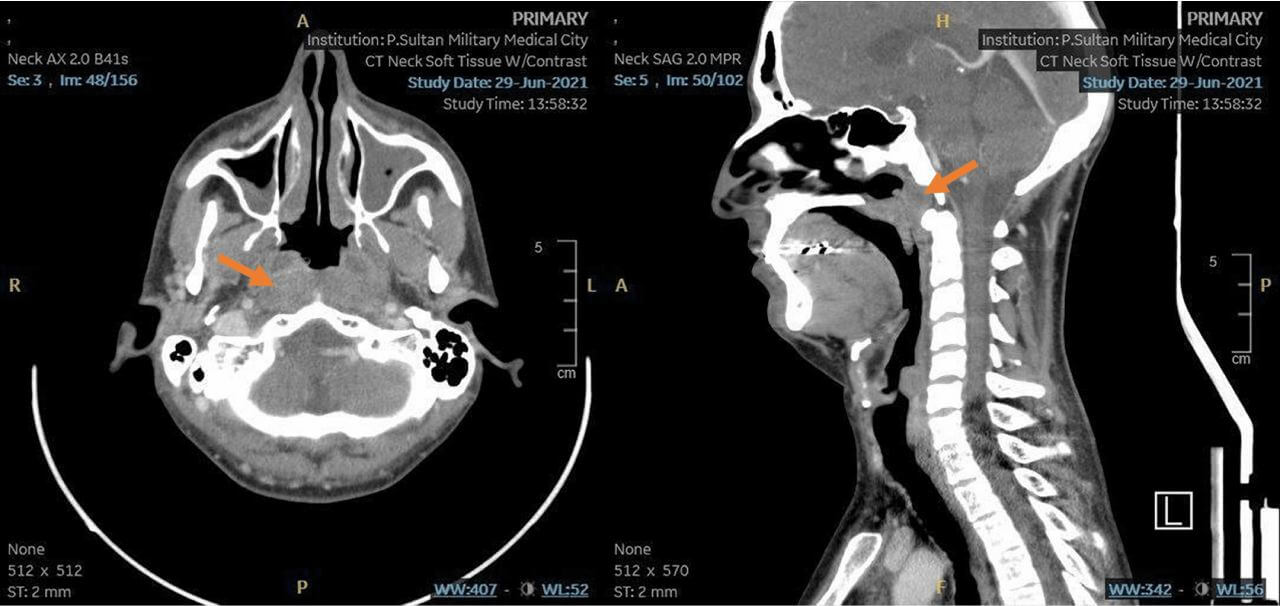
Standard treatment methods for nasopharyngeal cancer
Modern approaches that allow for effective treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer are based on a combination of radiation therapy with systemic treatment and individual selection of therapy depending on the stage of the disease. Nasopharynx carcinoma treatment is in most cases based on non-surgical approaches, which is due to the complex anatomy of the nasopharynx and the typical late detection of the disease. That is why effective treatment and management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma involves a combination of radiation and systemic therapy, and treatment and management for nasopharynx carcinoma should be carried out in a multidisciplinary approach. Surgical treatment is rarely used and is considered only in isolated cases of small primary tumors or in local recurrence after primary therapy [6].
Radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal cancer
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiation therapy is the basis of treatment, and modern protocols allow to achieve high local control while minimizing toxicity. In patients with localized forms of the disease, therapy may be radical, while advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma requires combined regimens. Rosenmuller's fossa is the most frequent site of nasopharyngeal tumor, accounting for over 80% of nasopharynx carcinoma cases, with the tumor remaining unilateral for up to 90% of cases even as it grows [7]. A particularly complex clinical category is stage 4 nasopharynx carcinoma, in which standard treatment options for stage IV nasopharyngeal cancer are used, including chemoradiotherapy and systemic treatment. Photodynamic therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma can be used in selected clinical cases as a local treatment method, allowing for targeted action on tumor tissue with minimal damage to surrounding structures.
Chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal cancer
In cases of a common process or high risk of progression, an important role is played by induction chemotherapy nasopharyngeal cancer, which can improve disease control and influence subsequent treatment tactics. It is in stage 4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma (cancer of the nasopharynx) that induction chemotherapy is often used as part of the standard approach.
Clinical manifestations of the disease, including symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma signs and symptoms, are usually correlated with the stage of the process and often cause the patient to seek medical help. Survival rate of nasopharyngeal carcinoma data suggest that treatment outcomes improve significantly with early diagnosis and treatment in specialized settings [8].
The optimal results of nasopharynx carcinoma treatment are achieved in the conditions of specialized nasopharynx carcinoma clinics or nasopharyngeal cancer treatment centers, where modern technologies and standardized protocols are available. Such institutions are often considered by patients as the best cancer center for nasopharyngeal carcinoma or the best hospital for nasopharyngeal cancer, especially in complex or common forms of the disease.
When choosing a medical institution, patients are also interested in the cost of nasopharyngeal cancer, which depends on the stage of the disease, the amount of therapy and the level of the medical center. The experience of stage 4 nasopharyngeal cancer stories emphasizes the importance of timely referral to specialized centers, where it is possible to individualize treatment even in the late stages of the disease.
Innovative treatment methods for nasopharyngeal cancer
Dendritic cell therapy for nasopharyngeal cancer
Current cancer of nasopharynx treatment is gradually moving beyond surgery, radiation and chemotherapy alone. Innovative therapies in Germany are actively developing in leading European clinics, which are aimed not only at destroying the tumor, but also at activating the body's own protective mechanisms.
One such approach is dendritic cells cancer treatment – immunotherapy, which works by training the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. The Nobel Prize was awarded in 2011 for discovering the role of dendritic cells and laying the foundations of dendritic cell therapy in immunology. Dendritic cells – are "conductors of the immune response": they show T-cells which cells in the body are dangerous. During therapy, blood cells are taken from the patient, in laboratory conditions, activated dendritic cells are created from them, which introduce the immune system to tumor antigens, after which these cells are returned to the patient as a vaccine [9].
This approach does not replace the main treatment, but can be used as a supplement, especially in complex or common forms of the disease. That is why treatment for cancer in Germany often includes immune methods as part of an individual treatment plan. For patients diagnosed with nasopharynx carcinoma, treatment for nasopharynx cancer in Germany is becoming more and more relevant, where dendritic therapy is used in accordance with modern clinical protocols or within specialized programs.
Importantly, dendritic cells cancer treatment is usually well tolerated, has a lower risk of systemic side effects, and targets long-term immune control of the disease. That is why patients often look for best hospitals for nasopharyngeal cancer treatment, where such innovative approaches are available and multidisciplinary teams work.
Thanks to the development of innovative therapies in Germany, cancer of nasopharynx treatment is increasingly focused not only on tumor control, but also on maintaining the quality of life, personalizing therapy and using the potential of the patient's own immune system.
Nasopharynx carcinoma – is a disease in which standard treatments are not always sufficient, especially in the later stages. That is why immune approaches, in particular therapy with dendritic cells, today attract special attention. In this video – is an exclusive interview with Professor Hansauge, head of a clinic specialising in innovative dendritic cell therapy. The professor shares clinical experience, explains when immune therapy makes sense, whether it can be combined with chemo and radiation therapy, and for whom this approach can really be a chance.
Regional chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal cancer
In the treatment of nasopharynx cancer, an important role is played not only by the choice of drugs, but also by the method of their introduction into the body. The goal of treatment is to deliver drugs to the tumor as efficiently as possible and at the same time reduce the load on healthy organs. This is especially true when it comes to the cancer of nasopharynx, because nasopharynx is located next to vital structures.
An alternative option is intra-arterial administration of chemotherapy. This is a more local method, in which the drug is fed directly into the artery that feeds the tumor in the nasopharynx area. This approach makes it possible to achieve a high concentration of drugs precisely in the tumor zone and potentially reduce systemic toxicity. It can be considered in complex cases, in particular with nasopharynx cancer stage 4, when standard methods do not always give the desired effect.
The drug is administered briefly – usually within 5-12 minutes. There are several technical options for such administration: through a special port installed in the vessel, or through a temporary catheter that is inserted through the femoral artery. In certain, more complex cases, this method can be combined with additional blood flow restriction to further increase the effectiveness of treatment in the tumor area [10].
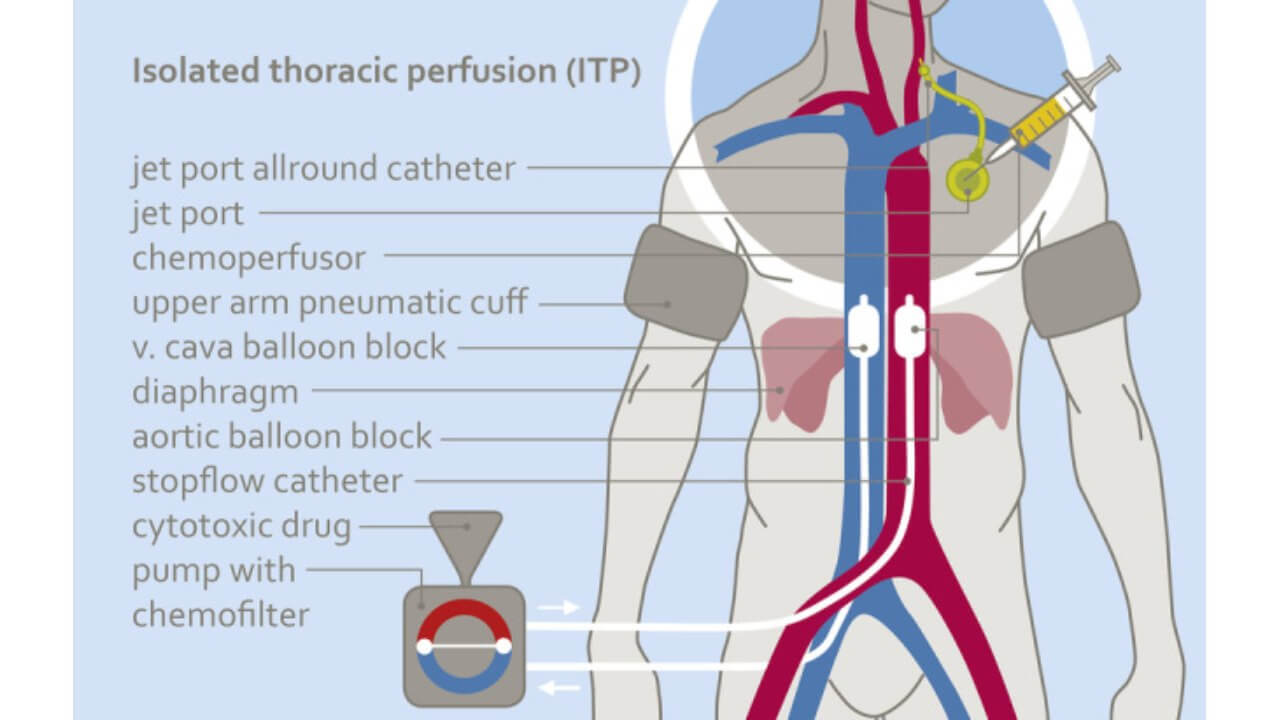
Intra-arterial chemotherapy is performed only in specialized conditions and requires extensive experience of the medical team. That is why it is important for patients to contact the nasopharynx cancer treatment center, where there is appropriate equipment and specialists who treat head and neck tumors.
Below is a comparative table showing key differences between standard and innovative treatments for nasopharynx carcinoma.
| Treatment type | Toxicity and side effects | Quality of life | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Moderate–high: nausea, fatigue, decreased immunity, nephro- and neurotoxicity (depending on the regimen) | Often temporarily reduced due to systemic side effects and repeated courses | Several months, cyclical treatment with interruptions |
| Radiation therapy | Significant: mucositis, dry mouth, swallowing disorders, otitis media, fatigue; late fibrotic changes are possible | Can decrease significantly during treatment and partially in the long term | Usually 5-7 weeks of daily treatment |
| Dendritic cell therapy | Low: usually mild local or flu-like reactions | Mostly preserved; absence of pronounced systemic toxicity | Long-lasting immune effect after a single injection |
| Regional chemotherapy | Lower systemic toxicity; possible local vascular complications | Better preserved with aiming action and faster recovery | Several short sessions; quick recovery between courses |
Treatment for stage 4 nasopharyngeal cancer
Stage IV nasopharyngeal carcinoma is characterized by an advanced tumor process and usually requires combination treatment with an emphasis on systemic therapy and symptom control to prolong life and maintain its quality. Treatment of metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer or recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer is possible and not limited to symptomatic care. The basis of therapy remains a combined approach using radiation and systemic therapy. At the same time, it is at this stage that innovative methods of treatment play an important role, which allow them to act more targeted and with less toxicity. These include modern chemotherapy regimens, local drug delivery methods, and immunotherapy, particularly dendritic cell therapy as an adjunct to standard care.
Treatment of the metastatic stage of nasopharynx carcinoma is always individualized and should be carried out in specialized centers with a multidisciplinary team. The availability of innovative approaches means that even at an advanced stage there are real options for treating and controlling the disease.
Treatment options for nasopharyngeal cancer in Germany
Treatment options for nasopharynx carcinoma in Germany combine standard oncology protocols with innovative methods, which is especially important in common or complex forms of the disease. Treatment is carried out in specialized centers with an individual approach.
One such method is dendritic cell therapy – immunotherapy aimed at activating one's own immune system to control tumor cells. It is usually used as an addition to the main treatment.
Another approach is regional chemotherapy, specifically intra-arterial chemotherapy, which allows drugs to be delivered directly to the tumor and reduce overall toxicity.
The combination of these methods extends treatment options for nasopharynx carcinoma in Germany, providing patients with real opportunities for active treatment even in the later stages.
Below is a comparative table of the cost of treating nasopharynx carcinoma in the world's leading countries which illustrates the main financial aspects related to different therapy protocols, access to innovative methods and level of medical care.
| Treatment type | Cost Germany | Cost USA | Cost GB | Cost Australia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | €80,000 - €150,000 full course | €100,000 - €180,000 full course | €90,000 - €165,000 full course | €45,000 - €120,000 |
| Radiotherapy | €28,000 - €42,000 | €40,000 - €80,000 | €35,000 - €65,000 | €25,000 - €50,000 |
| DC therapy | €20,000 - €38,000 | €40,000 - €100,000 | not available | not available |
| Regional chemotherapy | €18,000 - €75,000 per session | €37,000 - €150,000 | €30,000 - €118,000 | €30,000 - €80,000 |
History of a patient with nasopharyngeal cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer patient stories show that even in the late stages of the disease, individually tailored treatment and access to innovative methods can significantly improve disease control and quality of life. A 58-year-old patient was diagnosed with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma with cervical lymph node involvement (cT3 cN2 cM0, stage IVA) accompanied by nasal congestion, pain and hearing loss.
Due to concerns about severe side effects, the patient abandoned standard chemoradiotherapy, choosing an organ-sparing alternative to – short-term regional intra-arterial chemotherapy with chemofiltration performed at a specialized center in Germany.
Upon completion of treatment, significant reduction of tumor and regional metastases, improvement of well-being and pain control without pronounced toxicity were noted. After more than three years of observation, the patient remains without signs of progression, summarizing the result with the words: "I feel control over my own life again".
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex cancer management programs in each case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized nasopharynx carcinoma treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets.
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you on the way of pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for nasopharynx carcinoma with leading specialists in this field.
Modern Cancer Treatment: Patient Journeys with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Send request for treatmentIn general, this is a relatively rare head and neck cancer, but in some regions the frequency is much higher; it is important that with nasopharynx cancer staging, not the earliest cancer stage is often detected.
There is usually no direct "inheritance", but family predisposition is possible; risk is more often associated with EBV and environmental factors rather than “transmission” of nasopharynx cancer cells as such.
Most often, this is non-keratinizing carcinoma, that is, advanced nasopharynx carcinoma is more common in histology than keratinizing variants.
Yes, it is a serious disease, because nasopharynx carcinoma spreads early due to lymph nodes and the proximity of critical structures in nasopharynx.
Yes, nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment is effective in many cases, especially when the diagnosis is established at the early stage of nasopharynx carcinoma.
The pace is individual, but early lymphogenic metastasis is characteristic: nasopharyngeal cancer cells can quickly turn into lymph nodes, that is, nasopharynx cancer spreads earlier than the patient expects.
Most often, cervical and retropharyngeal lymph nodes are affected first.
For early stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma, typical unilateral congestion of nasal cavity, sensation "full ear", hearing loss, periodic nosebleeds – are early nasopharynx carcinoma signs and symptoms.
Symptoms of nasopharynx carcinoma may include nasal congestion, spotting, sore throat, enlarged neck knots, headache; it is also described as "symptoms nasopharyngeal carcinoma".
Red flags: persistent unilateral nasal congestion, progressive hearing loss, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, bleeding with nasal cavity, neurological symptoms – typical nasopharynx carcinoma signs and symptoms.
EBV can alter the operation of nasopharyngeal cells, supporting chronic cell transformation and promoting the accumulation of mutations in cancer cells.
Diagnosis includes examination of the ENT organs, nasopharyngeal endoscopy, MRI/CT, sometimes PET-CT, and mandatory biopsy; this is the basis for accurate nasopharynx carcinoma staging.
Early diagnosis of – is attention to symptoms of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, rapid referral to endoscopy and MRI, and, if necessary, – EBV marker tests and control of suspicious lymph nodes.
With nasopharyngeal cancer stage IV, complete cure is not always possible, but treatment for stage 4 nasopharynx cancer often allows you to achieve long-term disease control.
Nasopharyngeal cancer stage IV progresses differently: the rate is affected by the volume of metastases, the response to cancer treatment and tumor biology, so the key is to quickly start standard treatment protocols.
For metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer, systemic therapy (chemo/immuno/target as indicated) is used, as well as local control of foci; this is included in nasopharynx cancer (nasopharynx carcinoma) treatment options.
Survival rate depends on nasopharynx cancer staging, response to nasopharynx carcinoma radiation and presence of metastases; best results – at early stage nasopharyngeal cancer.
Best treatment is determined individually: stage, nodes, EBV status and general condition; usually the basis is nasopharynx carcinoma radiation as part of the combined treatment and management for nasopharynx carcinoma.
Most often radiation therapy ± chemotherapy by stage, that is, standard treatment protocols.
No, operations are rare; nasopharynx cancer treatment options without primary surgery prevail.
Yes, there are new treatments and new therapies: precise methods of irradiation, immunotherapy, dendritic cells cancer treatment, as well as proton beam therapy nasopharynx carcinoma and in certain situations photodynamic therapy nasopharynx carcinoma.
No, surgery is not "mandatory"; most patients are treated with standard treatment protocols without surgery, and with recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer, decisions are made individually.
Advantages of treatment for nasopharynx cancer in Germany – access to high-precision diagnostics, multidisciplinary teams in nasopharynx cancer treatment centers, and innovative therapies in Germany (including proton beam therapy nasopharyngeal carcinoma and dendritic cells cancer treatment according to indications).
The cost of nasopharyngeal cancer depends on the cancer stage, the scope of examinations, radiation therapy, systemic treatment and hospitalization; in Germany, the price varies between centers and cancer treatment protocols.
The best choice of specialized best hospitals for nasopharyngeal cancer treatment or nasopharynx cancer treatment center, where there is experience in the treatment of head and neck cancer and modern level treatment options are available; for the patient, it is actually the best cancer center for nasopharyngeal carcinoma or the best hospital for nasopharyngeal cancer within the country/region.
The most effective nasopharyngeal cancer treatment options usually include radiation therapy (as nasopharynx carcinoma radiation) in combination with chemotherapy by stage, sometimes induction chemistry nasopharynx carcinoma in common forms, and selection of systemic therapy in metastatic or recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer; in selected cases, proton beam therapy nasopharynx carcinoma or other innovative therapies in Germany are added which often reflect stage 4 nasopharyngeal cancer stories and nasopharynx cancer patient stories with real examples of disease control.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Daria Sukhoruchenko. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Yudi Xiong, Mengting Yuan, Zhigang Liu et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Epstein-Barr Virus Status in the Chinese Population: A Multicenter Investigation. J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 20;12(8):3005. doi: 10.3390/jcm12083005. [DOI] [PubMed]
[2] J H Wang, H Zhu, Y F Shang et al. [Nasopharyngeal carcinoma with non-squamous immunophenotype: a clinicopathological analysis of 23 cases]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 8;51(6):500-505. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20211111-00816. [DOI] [PubMed]
[3] Subhra Kumari, Surabhi Pandey, Mamta Verma et al. Clinicopathological Challenges in Tumors of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: Our Experience. Cureus. 2022 Sep 13;14(9):e29128. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29128. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[4] Alfred L Weber, Sharif al-Arayedh, Asma Rashid. Nasopharynx: clinical, pathologic, and radiologic assessment. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2003 Aug;13(3):465-83. doi: 10.1016/s1052-5149(03)00041-8. [DOI] [PubMed]
[5] Julian Goh, Keith Lim. Imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2009 Sep;38(9):809-16. [PubMed]
[6] Raymond K Tsang, William I Wei. Salvage surgery for nasopharyngeal cancer. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Oct 24;1(1):34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2015.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[7] An-Chuan Li, Ying-Ying Zhang, Chi Zhang, De-Sheng Wang, Ben-Hua Xu. Pathologic study of tumour extension for clinically localized unilateral nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Should the contralateral side be included in the clinical target volume? J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2018 May 28. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12741. Online ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed]
[8] Prashant Gabani, Justin Barnes, Alexander J Lin et al. Induction chemotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Clinical outcomes and patterns of care. Cancer Med. 2018 Jul 14;7(8):3592–3603. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[9] Emily Nickles, Bhushan Dharmadhikari, Li Yating et al. Dendritic cell therapy with CD137L-DC-EBV-VAX in locally recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma is safe and confers clinical benefit. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Oct 18;71(6):1531–1543. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03075-3. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[10] Karl R Aigner, Emir Selak, Kornelia Aigner. Short-term intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy for head and neck cancer patients maintaining quality of life. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Oct 31;145(1):261–268. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2784-4. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[11] Alshahrani E H, Ismail A (April 18, 2023) Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Presenting With Occipital Headache as a Sole Symptom in a Young Adult Male: A Case Report. Cureus 15(4): e37801. doi:10.7759/cureus.37801. [DOI]
Read:
Comprehensive Guide to Head and Neck Cancers
Comprehensive Guide to Oral Cancer Treatment
Tonsil Cancer Treatment: Guide to the Most Advanced Therapy Options
Не знаете, с чего начать?
Свяжитесь с Booking Health