Рак яичников – одно из наиболее распространенных гинекологических злокачественных заболеваний у женщин во всем мире. Согласно последним статистическим данным, рак яичников занимает восьмое место по распространенности среди женщин во всем мире – ежегодно диагностируется около 313 000 новых случаев.
Из-за отсутствия специфических симптомов заболевание очень трудно диагностировать на ранних стадиях. Следовательно, рак яичников зачастую выявляют на поздних стадиях, когда прогноз менее благоприятен. При этом показатели пятилетней выживаемости значительно варьируются в зависимости от стадии заболевания на момент постановки диагноза: у пациенток с I стадией рака яичников 5-летняя выживаемость достигает более 90%, тогда как при выявлении заболевания на III и IV стадии этот показатель составляет всего около 30%.
Существенную роль в успешности лечения тысяч пациенток с этим сложным диагнозом играет специализированная медицинская помощь, ведь благодаря грамотному подходу к разработке персонализированной схемы лечения надежда есть даже у женщины с поздними стадиями рака яичников.
Стандартные протоколы лечения
К стандартным методам лечения рака яичников относятся хирургия, химиотерапия и лучевая терапия, но облучение применяется не часто. Выбор метода лечения зависит от стадии рака, степени распространенности онкопроцесса и общего состояния пациентки.
Хирургическое вмешательство – главный метод лечения рака яичников, особенно на ранних стадиях заболевания. Обычно в ходе операции удаляются яичники, фаллопиевые трубы, матка и окружающие ткани. На поздних стадиях рака яичников проводится циторедуктивная операция, направленная на удаление опухолевой массы в максимально возможном объеме с целью повышения эффективности последующего курса лечения.
Химиотерапия – системный метод лечение, который может применятся после проведения хирургического вмешательства и на поздних стадиях рака. Терапия направлена на уничтожение оставшихся в организме раковых клеток, которые невозможно удалить хирургическим путем. Химиотерапия часто проводится несколькими циклами в течение нескольких месяцев. Этот вид лечения сопровождается серьезными побочными эффектами: повышенной утомляемостью, тошнотой, выпадением волос.
Лучевая терапия – роль этого метода в лечении рака яичников весьма ограничена. Из-за ничтожно малой эффективности облучения при поражении органов малого таза и потенциального риска повреждения здоровых тканей лучевая терапия при раке яичников проводится довольно редко. В основном облучение применяется в паллиативных целях для облегчения симптоматики на поздних стадиях заболевания, например, купирования болевого синдрома и остановки кровотечений.
Эти традиционные методы составляют основу лечения рака яичников, но при их применении женщины сталкиваются с серьезными побочными эффектами и подвергаются высокому риску развития рецидива онкологи. Такое положение вещей послужило стимулом к разработке инновационных видов терапии, которые смогли бы улучшить долгосрочные результаты лечения и повысить качество жизни пациенток.
Инновационные методы лечения
Благодаря стремительному развитию направления онкологии сейчас в арсенале врачей есть новаторские методики лечения рака яичников, дополняющие традиционные терапевтические протоколы. Эти прогрессивные методы лечения позволяют прицельно воздействовать на опухолевый очаг при минимизации побочных эффектов. К особо перспективным инновационным методам лечения прогрессирующих стадий рака относятся интервенционные вмешательства под визуальным контролем, терапия дендритными клетками, HIPEC (гипертермическая интраперитонеальная химиотерапия) и PIPAC (интраперитонеальная аэрозольная химиотерапия под давлением). Клинические исследования демонстрируют, что эти лечебные процедуры обеспечивают значительные преимущества для пациенток с поздними стадиями рака яичников или рецидивом онкопатологии, особенно при ограниченной эффективности традиционных методов лечения.
Интервенционная радиология
Терапевтические возможности в области интервенционной радиологии охватывают ряд минимально инвазивных процедур, которые приобретают все более важную роль в области онкогинекологии, особенно при лечении пациенток с раком яичников на поздних стадиях или с рецидивами заболевания. Эти таргетные интервенционные вмешательства под визуальным контролем используются как в качестве самостоятельного метода лечения, так и в качестве дополнения к традиционным видам терапии. Благодаря высокоточному воздействию непосредственно на онкологический очаг и минимальному повреждению окружающих тканей интервенционные методики используются в паллиативных целях и помогают добиться контроля над заболеванием у пациенток с ограниченными возможностями лечения.
Термоабляция – этот метод относится к числу наиболее часто применяемых минимально инвазивных процедур при лечении рака яичников. Деструкция опухоли происходит за счет воздействия на нее высокой температурой. На сегодняшний день лучше всего себя зарекомендовали два вида термоабляции: терапия высокоинтенсивным сфокусированным ультразвуком (HIFU), при которой разрушение опухоли достигается посредством прицельного наведения на нее ультразвуковых волн, и лазерная интерстициальная термотерапия (LITT), терапевтический эффект при которой обеспечивается за счет воздействия на опухолевый очаг лазерной энергией.
Изначально эти методы термоабляции предназначались для лечения доброкачественных заболеваний и локализованных опухолей, но сейчас их сфера применения расширилась и они также активно используются в области онкогинекологии. Последние исследования показали, что термоабляция позволяет достичь локального контроля опухоли у 82% пациенток с рецидивирующим раком яичников. Кроме того, термическая абляция вторичных опухолей способствует улучшению показателей беспрогрессивной выживаемости более чем в 70% случаев, что особенно важно при ограниченном количестве вторичных метастатических поражений.
Криоабляция – техника, предполагающая прицельное воздействие на злокачественные клетки экстремально низкими температурами с целью их необратимого повреждения. Не так давно криоабляция считалась более перспективным методом лечения других видов рака, но сейчас она все чаще рассматривается в контексте лечения рака яичников. Согласно предварительным данным, полученным в ходе исследований, криоабляция в комбинации с системной терапией повышает показатели беспрогрессивной выживаемости более чем у 80% женщин с раком яичников, при этом обеспечивая низкий профиль осложнений.
Криоабляция также проводится в комплексе с иммунотерапией для лечения вторичных опухолей в легких после безуспешной системной терапии. Благодаря минимальной инвазивности процедуры и ее благоприятному профилю безопасности она используется для высокоточного уничтожения метастатических поражений с труднодоступной локализацией в рамках паллиативного лечения.
Трансартериальная химиоэмболизация (TACE) – еще один консервативный и безопасный малоинвазивный метод лечения метастазов в печени при раке яичников. Данная интервенционная процедура обеспечивает двойной терапевтический эффект: таргетную доставку химиопрепаратов и эмболизацию кровоснабжающей опухоль артерии. В результате проведения TACE метастатические очаги лишаются кровоснабжения, после чего на них прицельно воздействуют высококонцентрированной дозой противоопухолевых препаратов. Процедура играет особо важную роль в лечении пациенток с неоперабельными метастазами в печени и при отсутствии адекватного ответа на системную химиотерапию, выступая в качестве эффективного альтернативного варианта терапии при невозможности проведения хирургической операции.
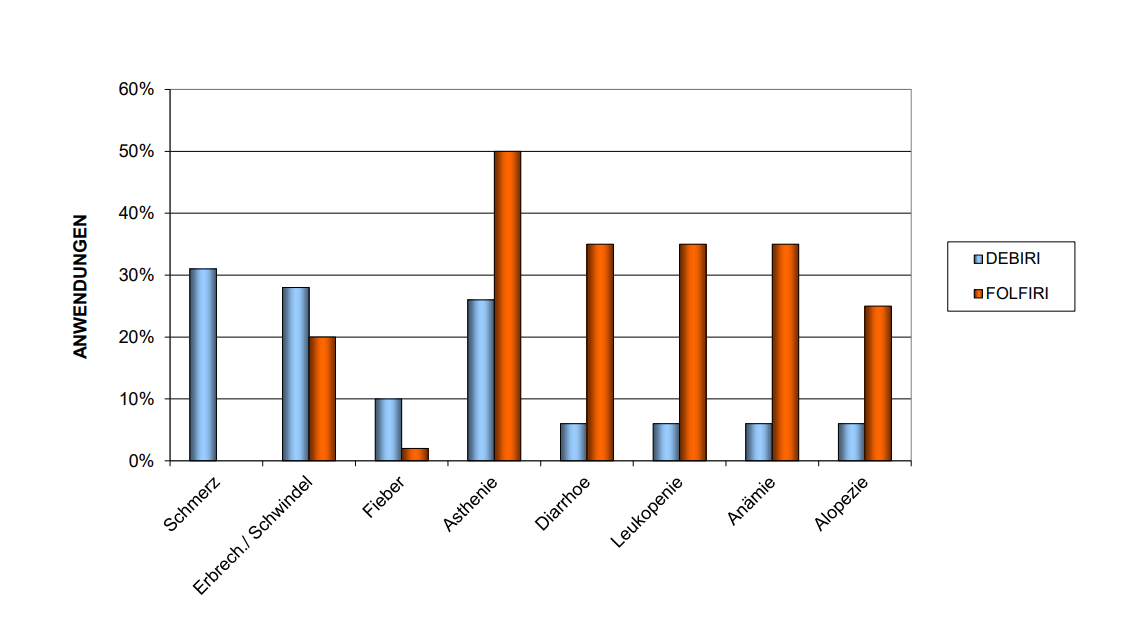
**DEBIRI = TACE, FOLFIRI = IV therapy; при проведении лечения по схеме DEBIRI у 90% пациенток наблюдается улучшение качества жизни на период 32 недель
Электрохимиотерапия (ЭХТ) при раке яичников
ЭХТ использует электрические импульсы, чтобы делать мембраны раковых клеток более проницаемыми. Благодаря этому химиопрепараты проникают внутрь в концентрациях, нереальных при стандартном внутривенном введении – это революционный механизм действия.
Врачи сочетают электрохимиотерапию с изолированной перфузией у пациенток с раком яичников, которым не помогло традиционное лечение. Электроды располагают вокруг опухоли, затем под анестезией подаютс импульсы и раковые клетки становятся проницаемыми. Затем во время сеанса изолированной перфузии через артериальные катетеры вводится высокодозная химиотерапия — поглощение препарата возрастает экспоненциально. Электрохимиотерапия в гинекологической онкологии использует принцип: злокачественные клетки более уязвимы к электрическим импульсам, чем здоровые ткани.
Побочные эффекты, как правило, незначительны, поскольку поскольку происходит локальное воздействие, пациентки быстро восстанавливаются. На сайте Booking Health можно найти информацию о клиниках и стоимости электрохимиотерапии в специализированных центрах. Стоимость электрохимиотерапии не всегда покрывается страховкой, поскольку метод инновационный; стоит уточнить это заранее.
Регионарная химиотерапия при раке яичников
Опубликованное исследование с участием 107 пациенток с раком яичников демонстрирует многообещающие результаты. При регионарной химиотерапии методом гипоксической изолированной перфузии брюшной полости медиана общей выживаемости составила 11,9 месяцев у пациенток с активным предшествующим лечением и резистентными формами рака – у пациенток, которым не помогли множественные циклы химиотерапии, со статусом ECOG 2-3 и неблагоприятным прогнозом. [8]
Профессор Карл Р. Айгнер разрабатывал и совершенствовал эту методику на протяжении 45 лет. Гипоксическая изолированная перфузия брюшной полости работает за счет изоляции кровотока в брюшной полости: баллонные катетеры устанавливаются в аорте и нижней полой вене, высокодозная химиотерапия вводится болюсно. Лечение проводится в течение 15 минут в условиях гипоксии – препараты демонстрируют усиленное противоопухолевое действие при отсутствии кислорода, многократно усиливая свою цитотоксичность. После перфузии химиофильтрация удаляет избыток химиопрепаратов для предотвращения их системной токсичности.
Результаты впечатляют: полная ремиссия – 17,3%, частичная ремиссия – 51,7%, общий благоприятный клинический эффект – 69%. Полное исчезновение асцита у 43% пациенток всего после двух перфузий – пациентки отмечают существенное облегчение болей. Качество жизни улучшилось в 74% случаев. Подавление костного мозга минимальное (степень 1-2 по ВОЗ), нейтропенической лихорадки не было, ладонно-подошвенный синдром не наблюдался ни у одной женщины. [8]
Это не теория – профессор Айгнер провел более 20 000 процедур перфузии. Никто в мире не имеет такого опыта. Приглашаем посмотреть интервью со знаменитым профессором:
Терапия дендритными клетками
Терапия дендритными клетками является персонализированным видом иммунотерапии, при котором для борьбы с раком яичников задействуется собственная иммунная система пациентки. Для проведения лечения осуществляется забор крови у пациентки с последующим извлечением из нее дендритных клеток, после чего их «обучают» распознавать специфические опухолевые антигены и повторно вводят пациентке с целью стимулирования таргетного иммунного ответа. В отличие от традиционной иммунотерапии при проведении вакцинации дендритными клетками практически не повреждаются здоровые клетки и на 80% улучшаются показатели выживаемости, особенно на поздних стадиях онкозаболевания, при которых классические методы лечения менее эффективны.
Основу этой терапии заложил лауреат Нобелевской премии доктор Ральф Штейнман, чья научно-исследовательская деятельность в корне изменила принципы иммунотерапии рака. Представляем вашему вниманию эксклюзивное интервью с профессором Франком Гансауге – экспертом в области проведения терапии дендритными клетками с более чем 22-летним клиническим опытом. В нем специалист рассказывает об особенностях проведения терапии дендритными клетками и об исключительной эффективности метода при его сочетании с лучевой терапией и химиотерапией, а также делится историями об успешном лечении пациентов из личного опыта.
В познавательном интервью с профессором Гансауге представлена полезная информация о научных основах терапии дендритными клетками, показателях успешности лечения этим методом и его роли в лечении рака в будущем.
Профессор Ганcауге раскрывает секреты лечения рака дендритными клетками: от науки к практике
HIPEC (гипертермическая интраперитонеальная химиотерапия)
HIPEC (гипертермическая интраперитонеальная химиотерапия) – инновационный метод лечения прогрессирующего рака яичников, который отличается особой эффективностью при лечении III и IV стадий заболевания. В отличие от системной химиотерапии, HIPEC предполагает введение разогретого до высоких температур раствора химиопрепаратов непосредственно в брюшную полость во время операции после хирургического удаления всех видимых опухолей. Нагревание химиопрепаратов до 41-43°C улучшает их проникновение в микроскопические остаточные раковые новообразования, которые невозможно увидеть невооруженным глазом в ходе хирургического вмешательства. Таким образом, HIPEC способствует существенному снижению частоты рецидивов рака и повышению показателей выживаемости до 50%. Преимуществом этого локализованного метода лечения также является минимальное количество системных побочных эффектов, благодаря чему для многих пациенток он является более безопасным вариантом терапии, нежели классическая химиотерапия.
Доктор Михаэль Липп – ведущий врач Отделения абдоминальной и колоректальной хирургии при Клинике Асклепиос Бармбек Гамбург. В своем интервью он рассказывает о том, как HIPEC способствует улучшению результатов хирургического лечения, о критериях отбора пациенток и важной роли эмоциональной устойчивости женщины в период восстановления после процедуры.
Ведущий немецкий хирург доктор Липп о преимуществах HIPEC в лечении рака
PIPAC (внутрибрюшная аэрозольная химиотерапия под давлением)
PIPAC (внутрибрюшная аэрозольная химиотерапия под давлением) – инновационный малоинвазивный метод лечения рака яичников на последних стадиях, занимающий особо важное место в лечении пациенток с обширным перитонеальным метастазированием, которым противопоказано хирургическое вмешательство или у которых традиционная химиотерапия не дала желаемого результата. В отличие от процедуры HIPEC, при проведении которой в ходе операции в брюшную полость пациентки вводится нагретый жидкий раствор химиопрепаратов, PIPAC предполагает распыление химиопрепаратов в виде аэрозоля под давлением посредством лапароскопического доступа, благодаря чему лекарственные средства лучше распределяются в патологическом очаге, глубже проникают в ткани и значительно снижается профиль системных побочных эффектов. При необходимости процедура PIPAC может проводится повторно каждые 4-6 недель, в силу чего она расценивается как эффективный метод для достижения долгосрочного контроля над заболеванием и улучшения качества жизни женщины с раком яичников.
Согласно результатам клинических исследований, PIPAC помогает снизить опухолевую нагрузку, облегчить симптоматику и потенциально уменьшает объем опухоли до того показателя, при котором становится возможным проведение HIPEC или циторедуктивной операции. PIPAC часто используется в качестве дополнительного или паллиативного метода лечения, но при этом внедрение процедуры в клиническую практику все же является большим шагом вперед в лечении рецидивирующих или неоперабельных форм рака яичников.
Сравнительный анализ и статистика
Чтобы оценить потенциал традиционных и инновационных методов лечения необходимо сравнить их эффективность, продолжительность курса лечения и профиль побочных эффектов. В этом поможет представленная ниже сравнительная таблица.
| Характеристики/Вид терапии | Показатели 2-летней выживаемости | Показатели ответа на лечение | Продолжительность курса лечения | Побочные эффекты |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Стандартные методы лечения | ~25% на поздних стадиях рака | Менее 10% | Несколько циклов | Тяжелые побочные эффекты (тошнота, утомляемость, выпадение волос, иммуносупрессия, раздражение кожи) |
| Инновационные методы лечения | ~60% на поздних стадиях рака | 45-65% | До 4 сеансов | Незначительные побочные эффекты (дискомфорт в месте проведения лечебной манипуляции) |
История пациентки об успешном лечении
Лучшим подтверждением успешности инновационного лечения рака яичников вакцинацией дендритными клетками, HIPEC и PIPAC являются реальные истории наших пациенток. Личный опыт женщин, испытавших на себе новаторские лечебные процедуры, является основанием для надежды и вселяет уверенность в успехе пациенткам, которые борются с этой сложной болезнью. Истории этих пациенток свидетельствуют о хороших шансах на выздоровление при лечении инновационными методами HIPEC, PIPAC и дендритно-клеточными вакцинами, что в свою очередь демонстрирует их большой потенциал в достижении ремиссии даже на поздних стадиях рака.
Одной из таких пациенток является Гретта Гаспарян, которая прошла лечение рака яичников 4 стадии в Клинике LDG Laboratories, Германия. Терапию лично курировал доктор Гансауге – руководитель клиники. Поскольку возможности лечения в родной стране пациентки практически себя исчерпали, ее семья обратилась за помощью в компанию Booking Health, которая оперативно организовала консультации с врачом, составила наиболее подходящую в случае Гретты программу лечения и оказала необходимую помощь в оформлении визы и организации поездки на лечение в другую страну.
Под чутким наблюдением профессора Гансауге пациентка прошла иммунотерапию дендритными клетками. На протяжении всего процесса лечения Гретта и ее семья получали всестороннюю поддержку со стороны специалистов Booking Health, включая услуги переводчика и помощь менеджеров по туризму, благодаря чему все прошло замечательно, не было никаких проблем.
Положительный опыт Гретты Гаспарян свидетельствует об эффективности терапии дендритными клетками и о важности профессиональной поддержки опытного оператора медицинского туризма в получении онкологической помощи передового стандарта.
Стоимость лечения рака яичников
Стоимость лечения рака яичников сильно варьируется в зависимости от стадии заболевания и проводимого курса терапии. Германия славится своими передовыми протоколами лечения рака, поэтому в этой стране пациентам предлагаются прозрачные цены и медицинское обслуживание высочайшего качества.
Как правило, лечение рака яичников 1 стадии включает хирургическое вмешательство и локализованную химиотерапию. На ранних стадиях также могут применяться лапароскопические вмешательства, которые являются минимально инвазивным и экономически выгодным вариантом лечения.
При раке яичников 2 стадии основу лечения зачастую составляет хирургическое вмешательство и системная химиотерапия. Расходы на лечение варьируются в зависимости от сложности операции и используемой схемы химиотерапии.
При поздних стадиях рака яичников, например, на 3 стадии онкологии, требуется более радикальное лечение: терапия дендритными клетками, циторедуктивная операция и HIPEC.
| Метод лечения | Германия | Великобритания | США |
|---|---|---|---|
| Стандартные методы лечения | €80 000 - €150 000 за полный курс | €90 000 - €165 000 за полный курс | €100 000 - €180 000 за полный курс |
| Инновационные методы лечения | €25 000 - €60 000 за полный курс | €70 000 - €120 000 за полный курс | €100 000 - €150 000 за полный курс |
*Цены могут варьироваться в зависимости от конкретного вида опухоли и проводимых лечебных мероприятий.
Поездка на лечение за границу с Booking Health
Самостоятельный поиск наилучшей тактики лечения с учетом вашей индивидуальной клинической ситуации – довольно сложная задача. Испытав на себе многочисленные курсы лечения, проконсультировавшись со множеством специалистов и испробовав различные терапевтические процедуры, вам может быть трудно сориентироваться во всей предоставленной врачами информации. В таком случае пациенты зачастую выбирают первый же предложенный вариант лечения или соглашаются на лечение с применением стандартизированных терапевтических протоколов, которое повлечет за собой множество побочных эффектов, вместо того, чтобы рассмотреть возможность терапии с помощью инновационных процедур.
Если вы хотите сделать осознанный выбор и получить лечение рака в соответствии с индивидуально разработанной для вас схемой с учетом особенностей вашей конкретной клинической ситуации, проконсультируйтесь с врачами-консультантами Booking Health. Компания Booking Health уже более 12 лет занимает ведущие позиции в сфере организации лечения за рубежом с применением новейших инноваций в медицине, поэтому ее специалисты обладают огромным опытом в составлении персонализированных комплексных программ лечения для каждого пациента. Booking Health пользуется репутацией авторитетной компании, которая предоставляет персонализированный подбор схемы лечения рака яичников 4 стадии и клиники с прямым бронированием приема в медицинском центре и полной поддержкой на каждом этапе лечения – от решения организационных вопросов до помощи в процессе лечения. Мы предлагаем:
- Оценку и анализ выписок пациентки
- Составление индивидуальной программы лечения
- Подбор подходящего медицинского учреждения для лечения
- Подготовку медицинской документации и ее направление в выбранную пациенткой для лечения клинику
- Консультации с врачами зарубежной клиники для разработки оптимальной медицинской программы на этапе подготовки к поездке на лечение
- Экспертные консультации во время пребывания в больнице
- Последующее консультирование пациентки после ее возвращения на родину по завершении медицинской программы
- Решение организационных вопросов в рамках подготовки к поездке на лечение за границу
- Координацию пребывания пациентки в другой стране, помощь в бронировании отеля или апартаментов на период лечения
- Помощь в оформлении визы и бронировании авиабилетов
- Услуги переводчика и персонального координатора, который будет с вами на связи 24/7
- Прозрачные цены на лечение без скрытых платежей
Здоровье – главная ценность в жизни каждого человека, доверять заботу о которой стоит лишь лучшим специалистам с богатым опытом и проверенной репутацией. Booking Health – это ваш надежный партнер, который оказывает всестороннюю помощь на пути к восстановлению здоровья и улучшению качества жизни. Свяжитесь с врачом-консультантом компании, чтобы узнать больше о возможностях персонализированного лечения метастатического рака яичников у ведущих экспертов с использованием инновационных методов.
Эффективное лечение рака: опыт пациентов Booking Health
Частые вопросы наших пациенток о раке яичников
Отправить запрос на лечениеДля выявления рака яичников проводится гинекологический осмотр, трансвагинальное УЗИ и анализ крови на онкомаркеры, в частности онкомаркер рака яичников CA-125. При обнаружении патологических изменений дополнительно выполняются визуализационные исследования (КТ или МРТ) и биопсия.
Какие профилактические обследования проводится для предотвращения или раннего выявления рака яичников?
Пациентке предстоит пройти трансвагинальное УЗИ и анализ крови на онкомаркер рака яичников CA-125. Пациенткам с высоким риском рекомендуется генетическое тестирование на мутации BRCA1 и BRCA2, поскольку они значительно повышают риск развития рака яичников.
Рак яичников – это онкологическое заболевание, поражающее яичники. Различают три основных вида этой онкопатологии: эпителиальные опухоли (наиболее распространенные), герминогенные опухоли и стромальные опухоли. Существует 4 стадии рака яичников – от первичной локализации новообразования в пределах яичников (I стадия) до его распространения на отдаленные органы (IV стадия).
Наивысшие шансы на излечение пациентка имеет при выявлении рака яичников на ранней стадии. При условии своевременного выполнения хирургического удаления опухоли и проведения химиотерапевтического лечения показатели выживаемости при раке яичников I стадии достигают 90%. На поздних стадиях этого онкологического заболевания повысить показатели выживаемости могут такие методы лечения, как HIPEC и терапия дендритными клетками, но полное излечение менее вероятно.
Зачастую ранние симптомы незначительны и по них сложно заподозрить рак яичников: вздутие живота, боли в животе, частые позывы к мочеиспусканию, проблемы с пищеварением. По мере прогрессирования заболевания симптомы становятся более выраженными: появляется болевой синдром в области таза, а также наблюдается повышенная утомляемость и потеря веса.
Рак яичников занимает восьмое место по распространенности среди женщин во всем мире. Ежегодно в мире диагностируется около 313 000 новых случаев заболевания, причем наибольшая заболеваемость наблюдается в развитых странах.
Да, генетические факторы играют важную роль в развитии этого онкозаболевания. Риск развития рака яичников повышается при наличии у женщины в генах мутаций BRCA1 и BRCA2. Женщины, у которых в семейном анамнезе присутствует рак молочной железы или рак яичников, подвержены более высокому риску, в связи с чем им следует пройти генетическое тестирование.
К основным методам лечения рака яичников относятся хирургия, химиотерапия и лучевая терапия – облучение используется довольно редко. Таргетная терапия, например лечение ингибиторами PARP, и иммунотерапия, например терапия дендритными клетками, также обладают довольно высокой эффективностью на поздних стадиях заболевания.
Для определения стадии рака яичников проводятся визуализационные исследования и выполняется биопсия. На I стадии онкопроцесс локализуется в пределах яичников, а на IV стадии отмечается распространение метастазов в отдаленные органы. На ранних стадиях основу лечения обычно составляют хирургическое вмешательство и химиотерапия, в то время как на поздних стадиях онкопатологии может потребоваться проведение HIPEC, таргетной терапии и иммунотерапии.
Хирургическое вмешательство предполагает удаление яичников, фаллопиевых труб, матки и сальника. С целью уменьшения размеров опухоли перед химиотерапией или HIPEC на поздних стадиях рака яичников проводится циторедуктивная операция.
Да, такая терапия существует. При раке яичников используется лечение такими таргетными препаратами, как ингибиторы PARP и бевацизумаб. Эти препараты направлены на нарушение механизмов роста и деления раковых клеток. Иммунотерапия, например терапия дендритными клетками, повышает способность иммунной системы распознавать и уничтожать раковые клетки.
Побочные эффекты лечения рака яичников различаются в зависимости от проводимого метода лечения. Химиотерапия может вызывать тошноту, выпадение волос и повышенную утомляемость, а после проведения процедуры HIPEC зачастую возникают боли в животе и усталость. Таргетная терапия обычно не вызывает серьезных побочных эффектов, но все же может спровоцировать гипертонию и утомляемость.
Выбирайте лечение за рубежом и Вы, несомненно, получите отличный результат!
Авторы:
Статья составлена под редакцией экспертов в области медицины, врачей-специалистов доктора Надежды Иванисовой и доктора Вадима Жилюка. Для лечения состояний, о которых идет речь в статье, необходимо обратиться к врачу; информация в статье не предназначена для самолечения!
С редакционной политикой, которая отражает наше стремление к точности и прозрачности, можно ознакомиться здесь. Перейдите по ссылке, чтобы ознакомиться с нашими правилами.
Источники:
National Ovarian Cancer Coalition
Читайте:
Борьба с распространенным раком яичников
Меню статьи:
Не знаете, с чего начать?
Свяжитесь с Booking Health